What Holds Homologous Chromosomes Together in Metaphase 1
If 2n 6 what is the probability of obtaining a gamete in which all the chromosomes are paternal ones. In meiosis I metaphase 1 can be found while in meiosis II metaphase 2 can be found.
Meiosis I Principles Of Biology
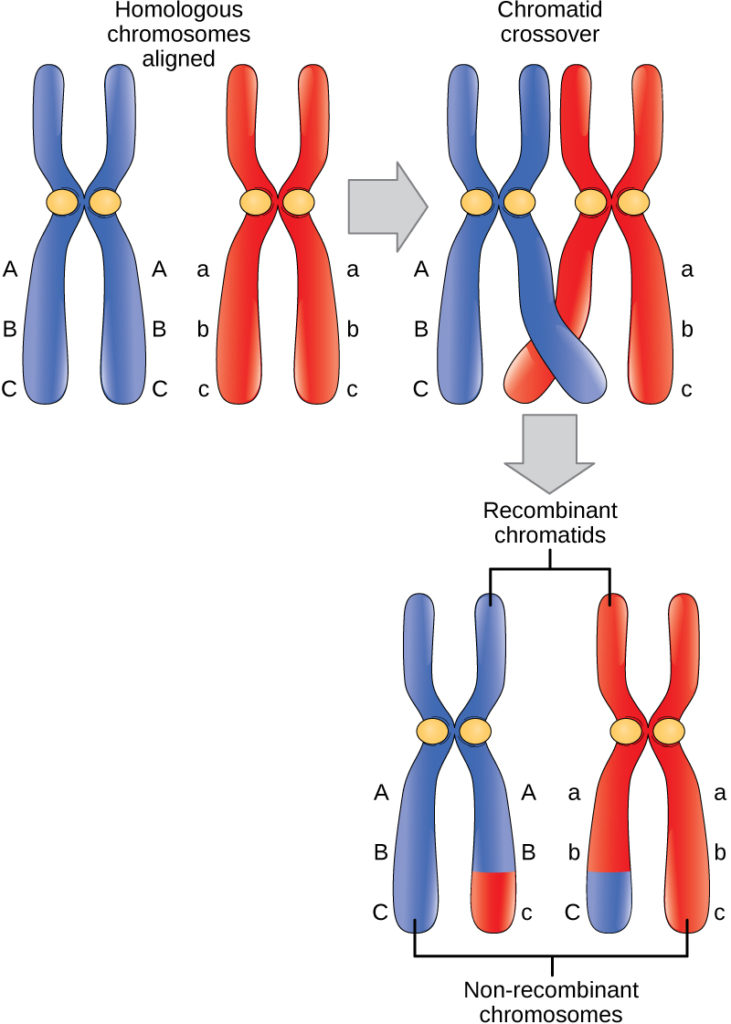
Recombination nodules are cross-over nodules composed of several proteins.

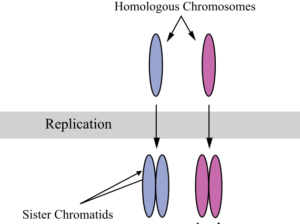
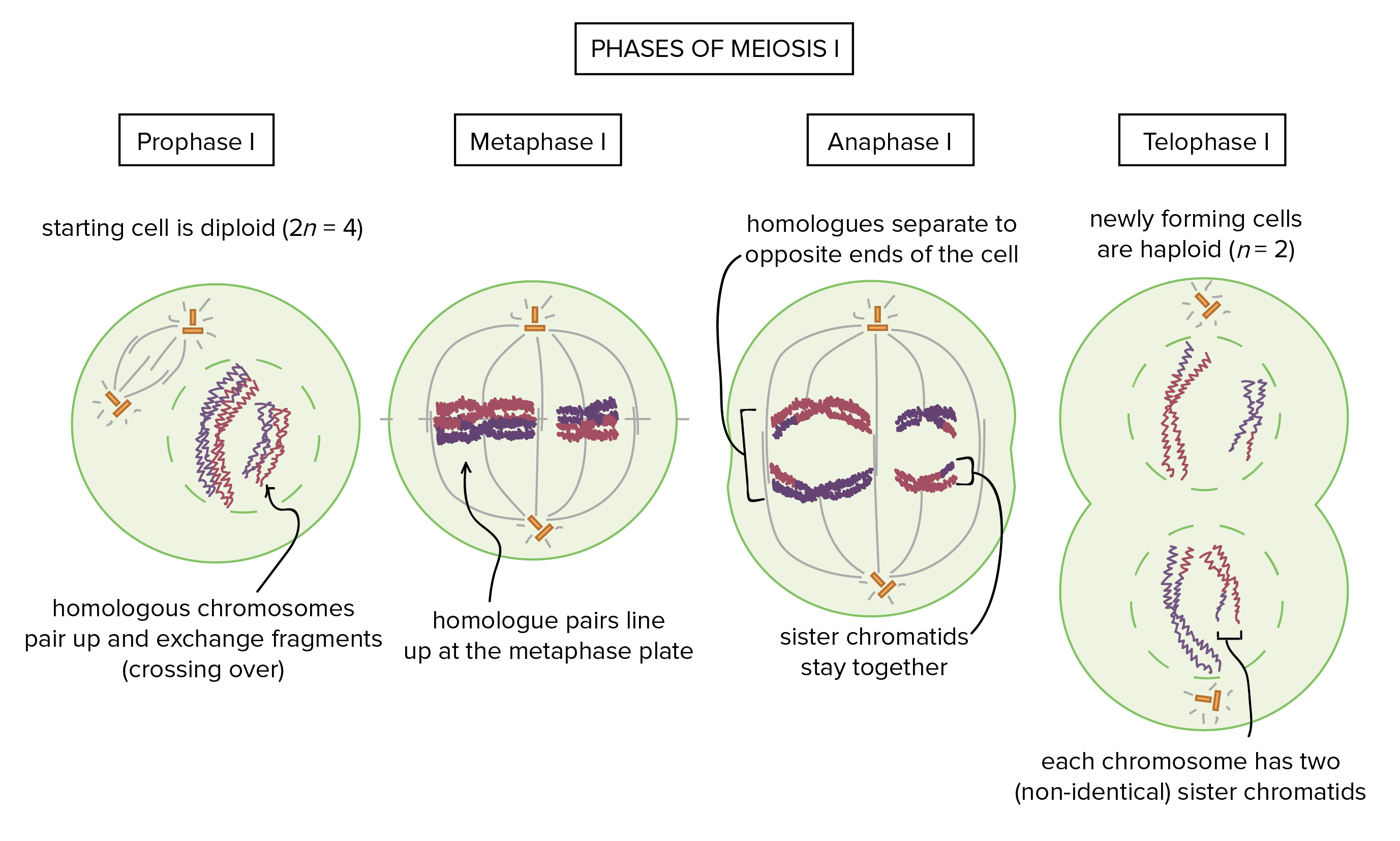
. In meiosis I homologous pairs of double stranded chromosomes are segregated. During anaphase I homologous chromosomes are separated and moved to opposite poles. During meiosis the homologous chromosomes come together during prophase I.
107 views View upvotes. This process of exchange between the chromosomes mixes the DNA of the two chromosomes and it is facilitated by protein structures called the synaptonemal complex. Each pair of homologous chromosomes separates.
The other side is turned inward toward. They are present along with synaptonemal complex the point of cross-over. Meiosis has numerous timescales in numerous organisms which could be affected by a number of elements together with temperature and environment of the organism.
During prophase I homologous pairs of chromosomes pair up in a process called synapsis to form tetrads. Sister chromatids remain attached to centromere and move as one unit towards each pole telophase 1 and cytokinesis. Kinetochore microtubules align homologous chromosomes along metaphase plate and random alignment of maternal and paternal homologs from each chromosome.
For example if the two homologous members of chromosome 1 are labeled a and b then the chromosomes could line up a-b or b-a. Both metaphase 1 and 2 are distinct from. - Chromosomes become more visible homologous chromosomes pair up crossing over occurs What occurs in metaphase 1 Bivalents line up randomly along the cells equator- random orientation spindle fibres from centrioles attach at the centromeres.
The alignment plays an important role as to which gene will be carried by the gametes. The process which transforms a diploid cell into four haploid cells at the time of gamete formation is known as meiosis. These cells each contain the haploid number of chromosomes.
Terminal chiasmata hold the homologous chromosomes together in metaphase 1 so that only one side of each centromere faces outward from the complex. In meiosis I the homologous chromosome pairs become associated with each other are bound together with the synaptonemal complex develop chiasmata and undergo crossover between sister chromatids and line up along the metaphase plate in tetrads with kinetochore fibers from opposite spindle poles attached to each. No at the time of metaphase II no homologous chromosomes pair up as in metaphase I.
These tetrads line up independently of each other random assortment in the equator of cell during metaphase I. In synapsis the genes on the chromatids of the homologous chromosomes are aligned with each other. Metaphase of meiosis one begins after crossing over occurs.
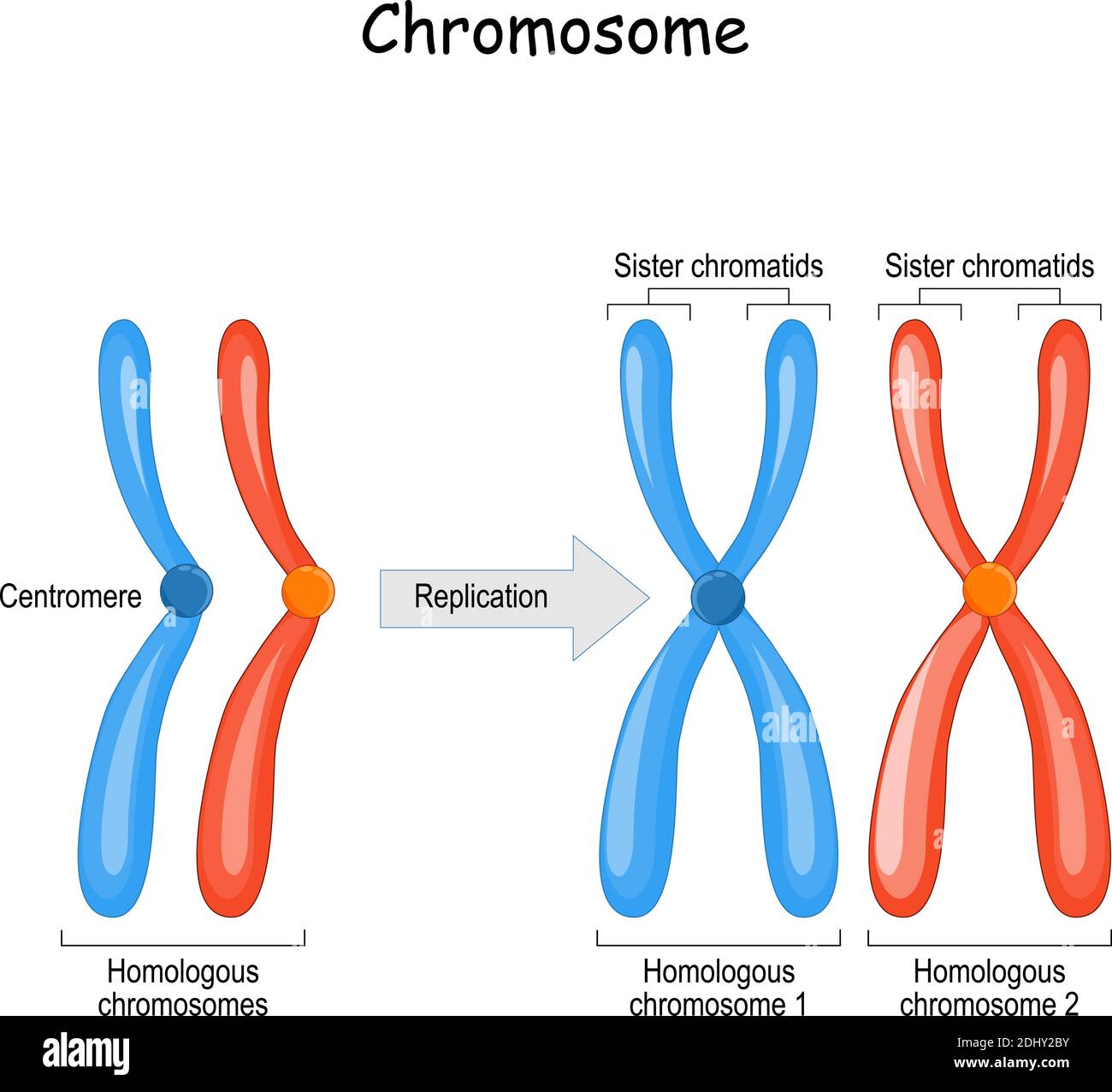
The synaptonemal complex a lattice of proteins between the homologous chromosomes forms at specific locations spreading to cover the entire length of the chromosomes. In mitotic metaphase a single chromosome pair of chromatids line up along the metaphase plate. The tight pairing of the homologous chromosomes is called synapsis.
Metaphase 1 Paired homologous chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. Meiosis and mitosis each have a prophase metaphase anaphase telophase and cytokinesis. By metaphase 1 the second stage of meiosis 1 the nuclear envelope has dispersed and the microtubules form a spindle just as in mitosis.
In these two cells meiosis II separates the sister chromatids producing two haploid gametes each. Microtubules attach to kinetochore Anaphase 1 homologous chromosomes separate and are pulled to opposite ends of the cell. 6 What part of the chromosomes do the spindle fibers attach to in order to move the chromosomes around.
During metaphase I the homologous chromosomes are arranged in the center of the cell with the kinetochores facing opposite poles. The areas where crossing over occurs are basically random which helps promote genetic diversity. Metaphase I is a stage where the homologous chromosomes align randomly at the equatorial plate with the kinetochore at opposite poles.
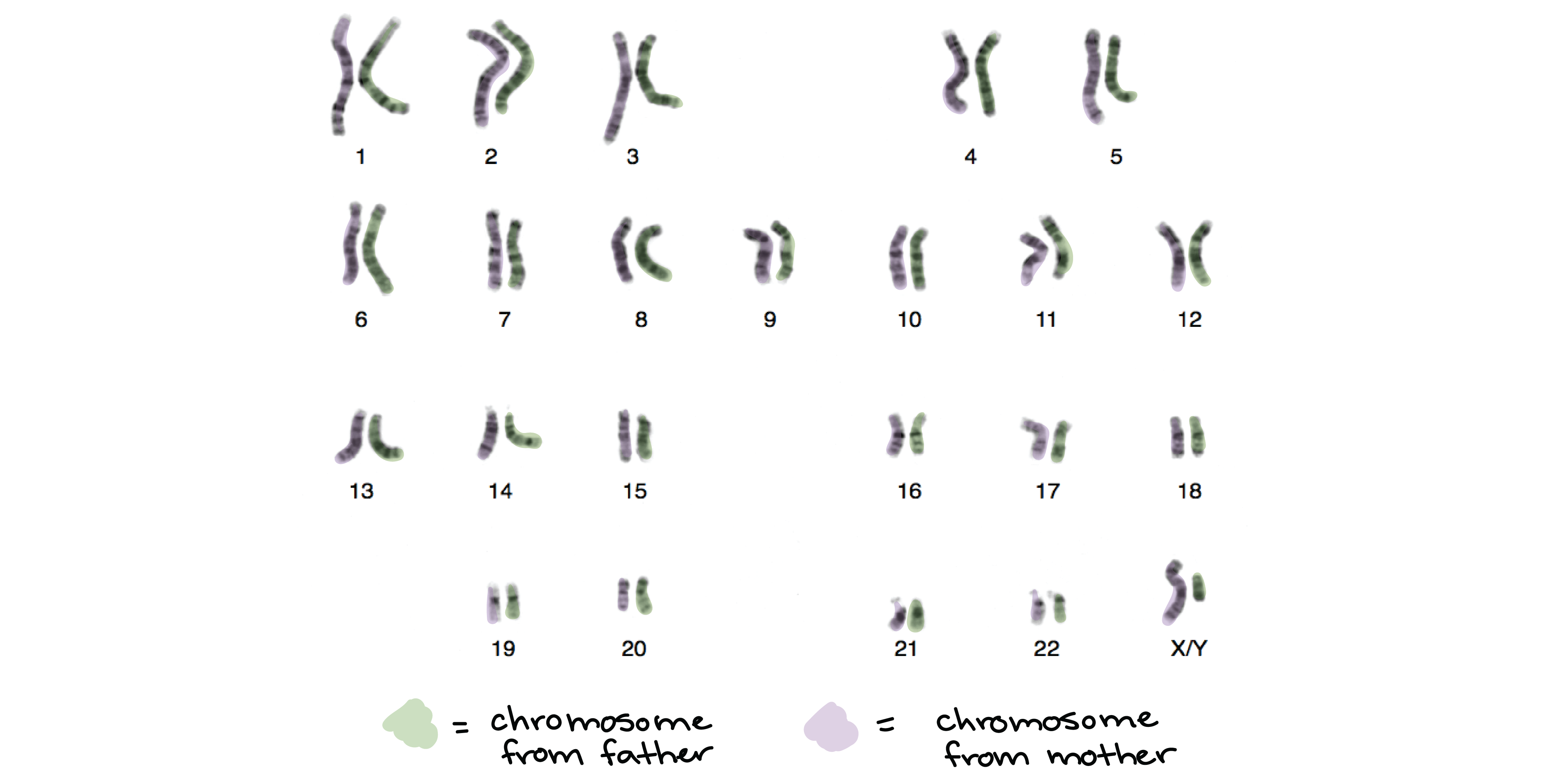
Metaphase I d in a diploid set of chromosomes one member of each pair of homologous chromosomes is derived from the father paternal and the other comes from the mother maternal. Anaphase 1 homologous chromosomes in each tetrad separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. The homologous pairs orient themselves randomly at the equator.
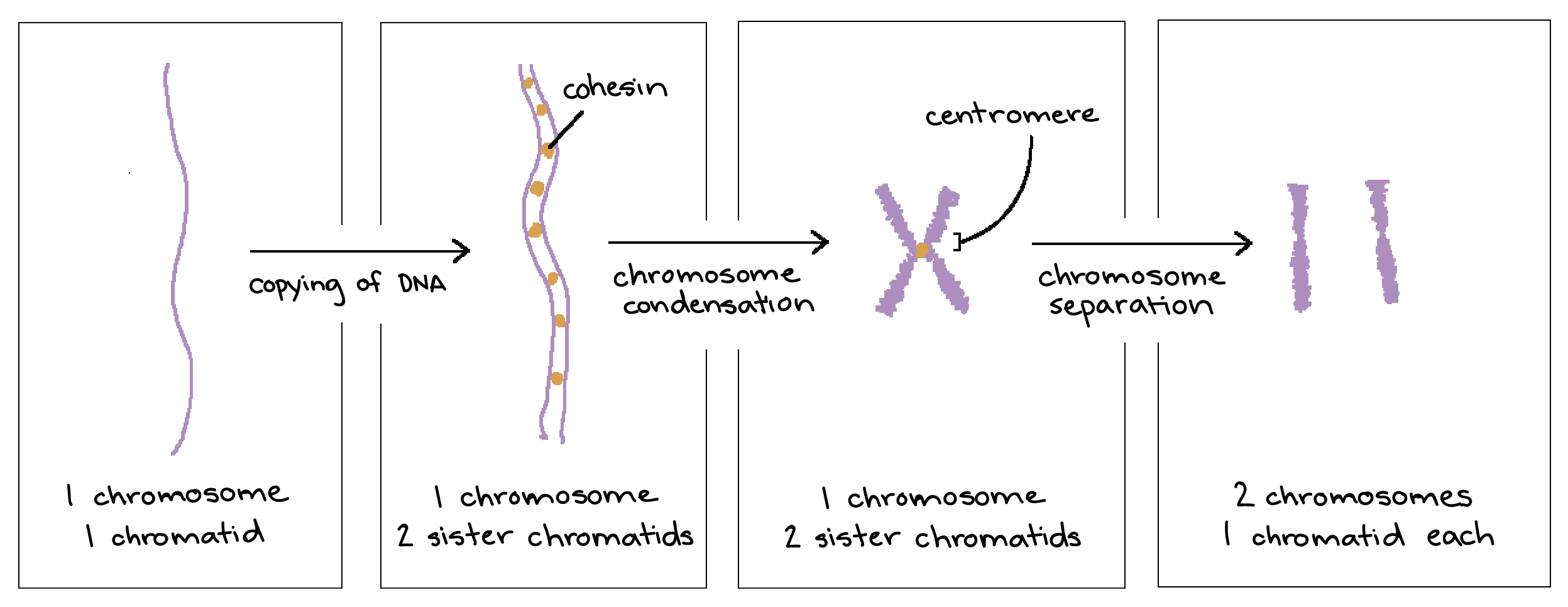
Pairs of homologous chromosomes align during a process called synapsis and form a tetrad four sister chromatids two. 3 What is the name of the structure that holds sister chromatids together. These are double stranded chromosomes where sister chromatids are copies.
7 What protein is responsible for holding the sister chromatids together and in what phase of mitosis does it break down.
Homologous Chromosomes High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy

Meiosis I Biology For Majors I

Meiosis I Biology For Majors I

Meiosis I Biology For Majors I

The Process Of Meiosis Biology I
Chromosomes Article Cell Cycle Khan Academy

Meiosis In Humans The Embryo Project Encyclopedia
Meiosis I Biology For Majors I
How Many Chromatids Are In A Chromosome Quora
Where Are Alleles Located On A Chromosome I Watched A Video That Explained That We Have 46 Chromosomes And 46 Chromatids I Always Imagined The Different Alleles Opposite Chromatids But We Typically
7 5 Sexual Reproduction Meiosis And Gametogenesis Biology Libretexts
Chromosomes Article Cell Cycle Khan Academy

New Solutions To Old Problems Molecular Mechanisms Of Meiotic Crossover Control Trends In Genetics
Meiosis Review Article Meiosis Khan Academy

Do Centromeres Divide In Meiosis Anaphase 1 Or 2 Quora
What Are Some Important Events That Occur In A Prophase Quora


Comments
Post a Comment